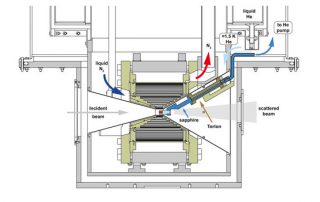
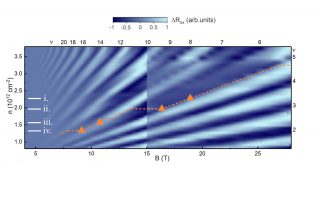
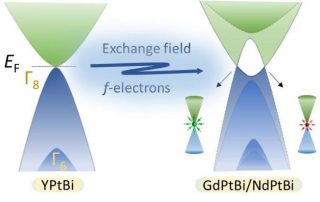
HIGH-FIELD CHARGE ORDER ACROSS THE PHASE DIAGRAM OF YBCO
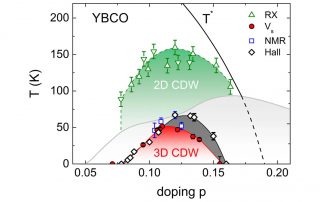
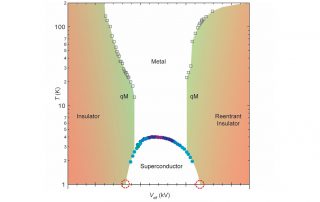
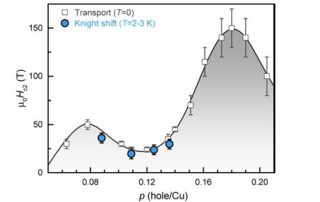
F. Laliberté, M. Frachet, S. Benhabib, B. Borgnic, C. Proust, D. LeBoeuf, LNCMI-Toulouse. In hole-doped cuprates there is now compelling evidence that inside the pseudogap phase, a charge density wave (CDW) breaks translational symmetry. In YBa2Cu3Oy (YBCO) this CDW emerges in two steps: a two-dimensional (2D) order found at [...]