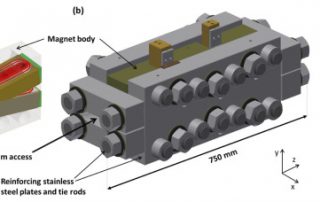
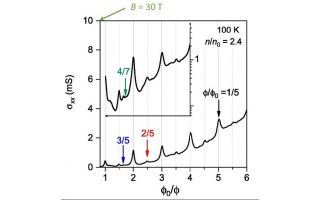
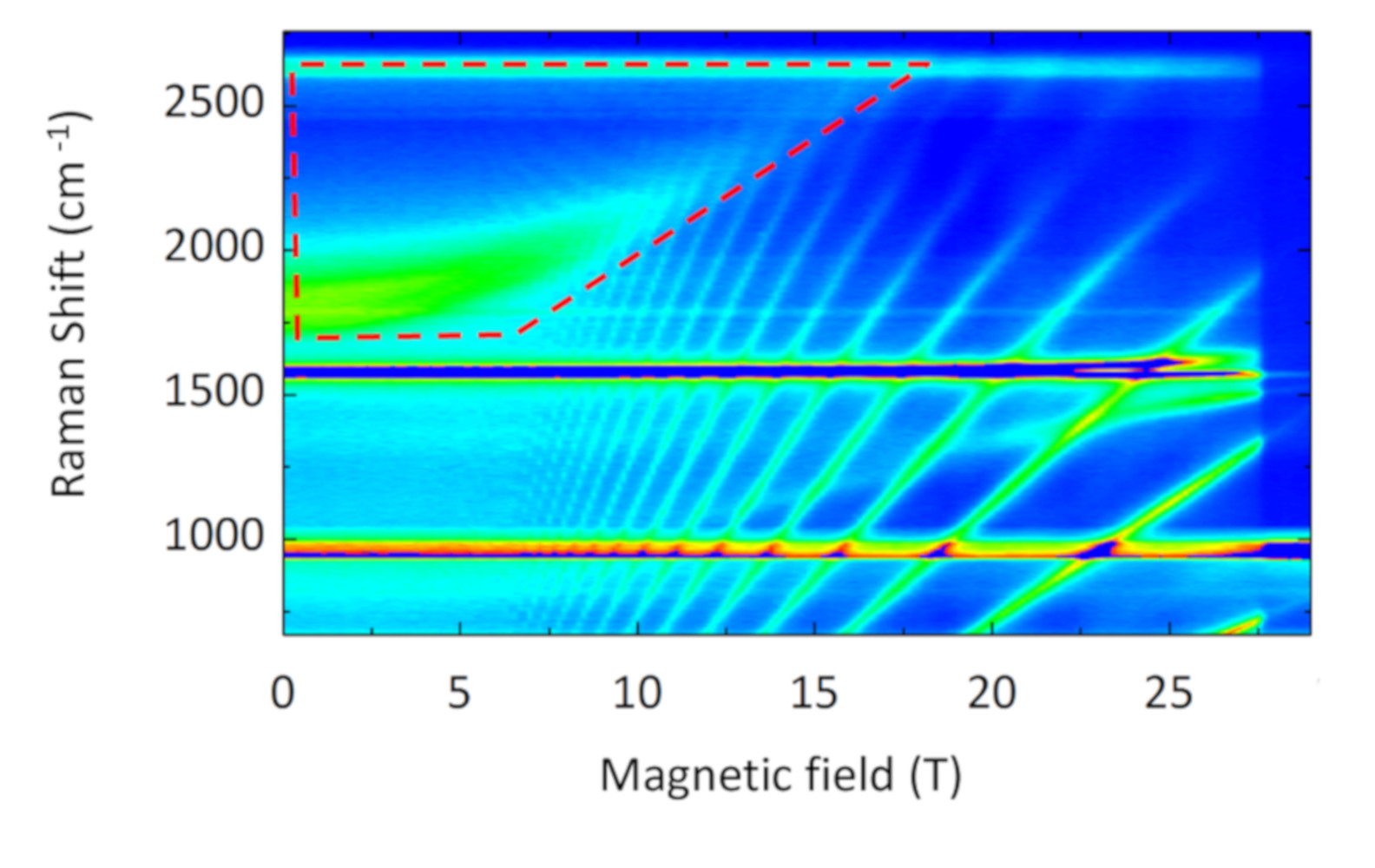
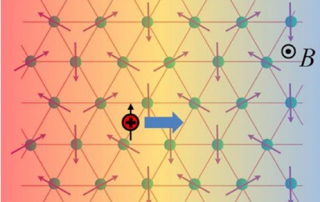
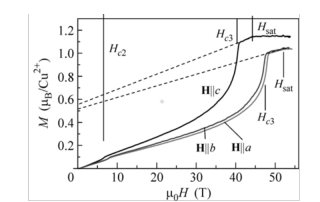
Electronic phases in high magnetic fields
Electrons are one of the fundamental constituents of solids, responsible for most of the important phenomena and applications in condensed matter physics. Therefore, understanding, controlling and manipulating electronic properties is still one of the great challenges of condensed matter research. An ideal testbed for this endeavour are high-quality two-dimensional [...]