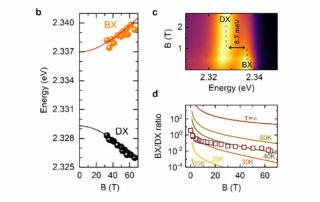
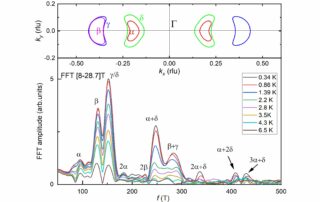
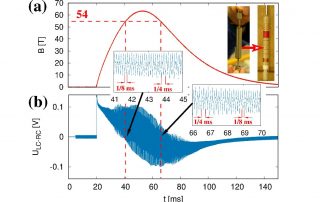
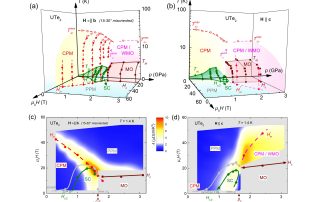
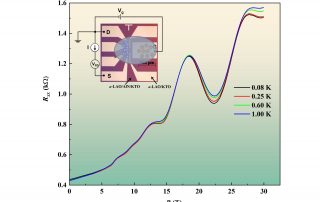
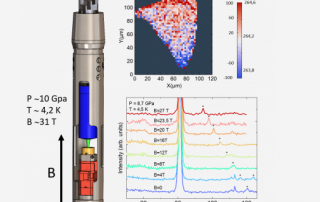
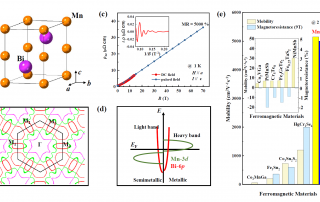
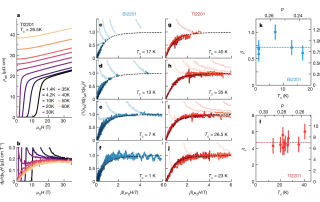
BRIGHTENING OF DARK EXCITONS IN 2D PEROVSKITES
Mateusz Dyksik, Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, Poland and Paulina Plochocka, LNCMI Toulouse. Optically inactive dark exciton states play an important role in light-emission processes in semiconductors because they provide an efficient nonradiative recombination channel. Understanding the exciton fine structure in materials with potential applications in light-emitting devices is, [...]