HIGH MAGNETIC FIELDS PROBE MULTIEXCITON STATES IN ORGANIC MATERIALS
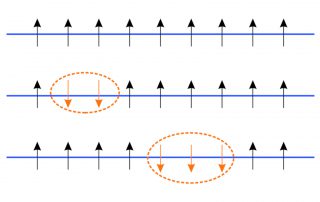
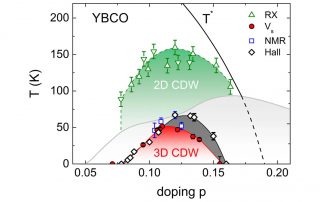
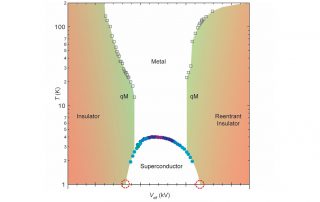
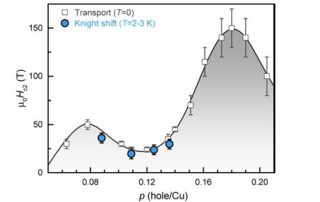
Leah Weiss, Sam Bayliss, University of Cambridge and Paulina Plochochka, LNCMI-Toulouse. Intermolecular coupling plays a key role in charge transport and excited-state dynamics in organic systems. A key example of the influence of intermolecular interactions is the process of singlet fission, which involves the production of two triplet excitons [...]