Matthew Bristow, Amalia Coldea, University of Oxford and William Knafo, LNCMI-Toulouse.
CaKFe4As4 belongs to a new family of 1144 iron-based superconductors. It is a clean and stoichiometric superconductor with a relatively high critical temperature of 35 K. This system lacks long-range magnetic order or a nematic electronic state at low temperatures. It is an ideal stoichiometric superconductor that is already optimally doped.
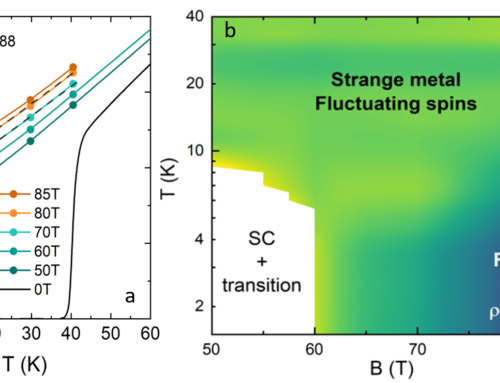
Due to the reduced symmetry compared with the 122 family, the Fermi surface of CaKFe4As4 is predicted to have up to ten different electron and hole sheets in which interband pairing between electron and hole pockets as well as the intraband pairing is possible (Figure 1f). CaKFe4As4 has an exceptionally large critical current density due to the strong point-like defects caused by local structural site effects as well as surface pinning. In order to understand the multi-band superconducting properties of CaKFe4As4, we have measured the upper critical fields for two orientations in magnetic fields up to 90 T using electrical-transport measurements (Figures 1a and 1b). These studies provide a complete upper critical field phase diagram of CaKFe4As4 indicating that it is isotropic at the lowest temperature (Figures 1c and 1d). We use a two-band model to describe the temperature dependence of the upper critical fields for both field orientations. The band coupling parameters indicate the presence of different competing pairing channels. Furthermore, at low temperatures, the in-plane upper critical field does not saturate but shows an upturn, consistent with the emergence of a Fulde-Ferrell-Larkin-Ovchinnikov (FFLO) state that can be stabilized in a clean system with shallow bands and a large Maki parameter (about 4.2) such as CaKFe4As4 (Figure 1e).
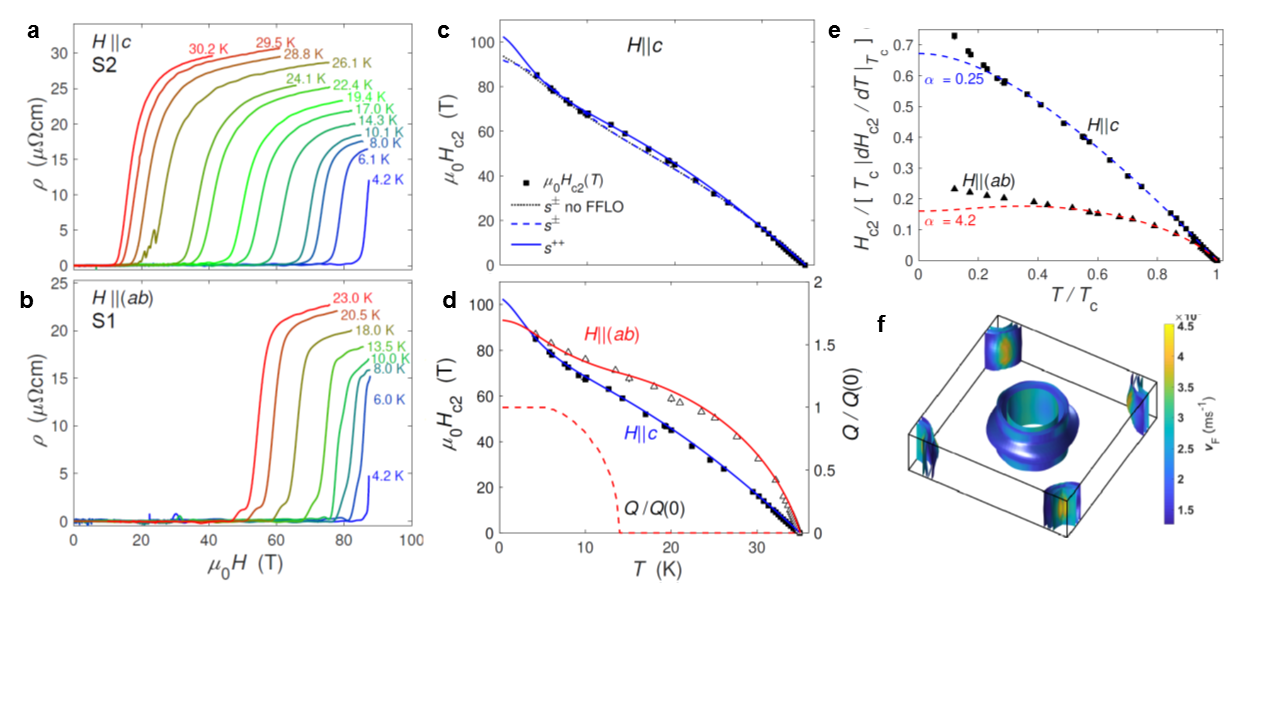
Figure 1: Resistivity versus magnetic field at constant temperatures measured in pulsed fields up 90 T, for (a) H || c (S2) and (b) H || (ab) (S1). The two-band model describes the temperature dependence of the upper critical field for the two different pairing symmetries for H || c in (c) and including the emergence of the FFLO state in (d). (e) Upper critical fields for the two field orientations scaled by the superconducting transition temperature, Tc, and the slope near Tc from the WHH model against the reduced temperature T/Tc. (f) Fermi surface of CaKFe4As4.
Competing pairing interactions responsible
for the large upper critical field in a stoichiometric iron-based superconductor CaKFe4As4,
M. Bristow, W. Knafo, P. Reiss, W. Meier, P. C. Canfield, S. J.
Blundell, and A. I. Coldea, Phys. Rev. B 101, 134502 (2020).
DOI: https://journals.aps.org/prb/pdf/10.1103/PhysRevB.101.134502
Contact: amalia.coldea@physics.ox.ac.uk